K-means算法:
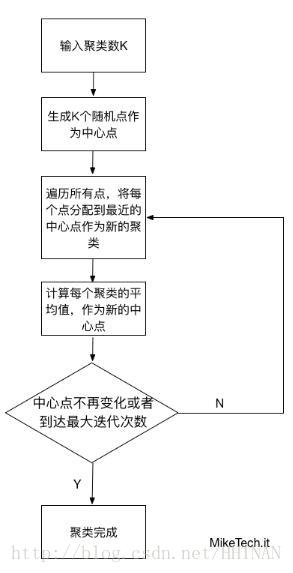
关于步骤:参考之前的博客
关于代码与数据:暂时整理代码如下:后期会附上github地址,上传原始数据与代码完整版,
各种聚类算法的对比:参考连接
Kmeans算法的缺陷
1.聚类中心的个数K 需要事先给定,但在实际中这个 K 值的选定是非常难以估计的,很多时候,事先并不知道给定的数据集应该分成多少个类别才最合适
2.Kmeans需要人为地确定初始聚类中心,不同的初始聚类中心可能导致完全不同的聚类结果。
#!usr/bin/env python#_*_ coding:utf-8 _*_import randomimport math'''
kMeans:2列数据对比,带有head
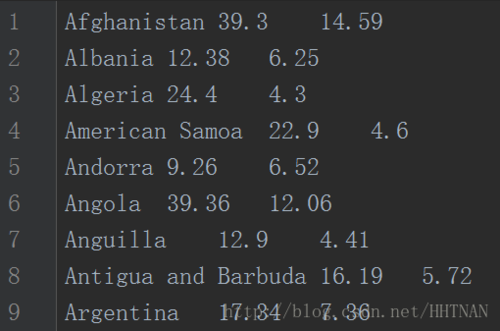
'''#1.load datadef importData():
f = lambda name,b,d: [name, float(b), float(d)] with open('birth-death-rates.csv', 'r') as inputFile: return [f(*line.strip().split('\t')) for line in inputFile]写入文件类型
#2. calculate Distance
def euclideanDistance(x,y):
return math.sqrt(sum([(a-b)**2 for (a,b) in zip(x,y)]))#L=points,def partition(points, k, means, d=euclideanDistance):
# print('means={}'.format(means))
thePartition = [[] for _ in means] # list of k empty lists
indices = range(k) # print('indices={}'.format(indices))
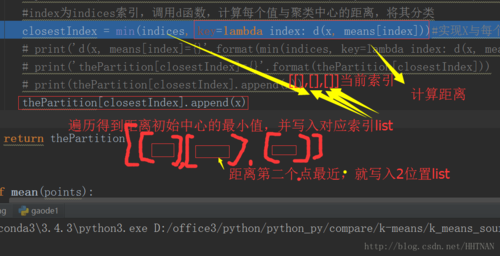
for x in points: #index为indices索引,调用d函数,计算每个值与聚类中心的距离,将其分类
closestIndex = min(indices, key=lambda index: d(x, means[index]))#实现X与每个Y直接的求解:key=lambda index: d(x, means[index])
thePartition[closestIndex].append(x) return thePartition#3.寻找收敛点def mean(points): ''' assume the entries of the list of points are tuples; e.g. (3,4) or (6,3,1). ''' n = len(points) # print(tuple(float(sum(x)) / n for x in zip(*points))) #*points将【[1,2],[2,3]】分割出来【1,2】 return tuple(float(sum(x)) / n for x in zip(*points)) #将最开始的[[4, 1], [1, 5]] 经过处理变成[(4, 1),(1, 5)]def kMeans(points, k, initialMeans, d=euclideanDistance): oldPartition = [] newPartition = partition(points, k, initialMeans, d) while oldPartition != newPartition: oldPartition = newPartition newMeans = [mean(S) for S in oldPartition] newPartition = partition(points, k, newMeans, d) return newPartition
#0.函数调用初始中心点
if __name__ == "__main__":
L = [x[1:] for x in importData()] # remove names
# print (str(L).replace('[','{').replace(']', '}'))
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt '''
plt.scatter(*zip(*L))
plt.show()
'''
import random
k = 3
partition = kMeans(L, k, random.sample(L, k)) #L是集合,K分类个数,random.sample(L, k)中心点
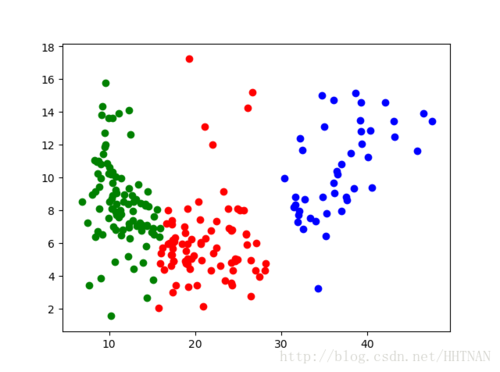
plt.scatter(*zip(*partition[0]), c='b')#[[],[],[]]
plt.scatter(*zip(*partition[1]), c='r')
plt.scatter(*zip(*partition[2]), c='g')
plt.show()点击查看更多内容
为 TA 点赞
评论
共同学习,写下你的评论
评论加载中...
作者其他优质文章
正在加载中
感谢您的支持,我会继续努力的~
扫码打赏,你说多少就多少
赞赏金额会直接到老师账户
支付方式
打开微信扫一扫,即可进行扫码打赏哦