In this tutorial, you will learn how to use SIGNAL and RESIGNAL statements to raise error conditions inside stored procedures.
MySQL SIGNAL statement
You use the SIGNAL statement to return an error or warning condition to the caller from a stored program e.g., stored procedure, trigger or event. The SIGNAL statement provides you with control over which information to return such as SQLSTATE value and message.
The following illustrates syntax of the SIGNAL statement:
SIGNAL SQLSTATE | condition_name SET condition_information_item_name_1 = value_1, condition_information_item_name_1 = value_2, etc;
Following the SIGNAL keyword is an SQLSTATE value or a condition name declared by the DECLARE CONDITIONstatement. Notice that the SIGNAL statement must always specify an SQLSTATE value or a named condition that defined with an SQLSTATE value.
To provide the caller with information, you use the SET clause. If you want to return multiple condition information item names with values, you need to separate each name/value pair by a comma.
The condition_information_item_name can be MESSAGE_TEXT, MYSQL_ERRORNO, CURSOR_NAME, etc.
The following stored procedure adds an order line item into an existing sales order. It issues an error message if the order number does not exist.
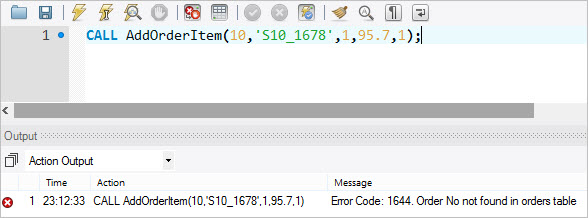
DELIMITER $$ CREATE PROCEDURE AddOrderItem( in orderNo int, in productCode varchar(45), in qty int, in price double, in lineNo int ) BEGIN DECLARE C INT; SELECT COUNT(orderNumber) INTO C FROM orders WHERE orderNumber = orderNo; -- check if orderNumber exists IF(C != 1) THEN SIGNAL SQLSTATE '45000' SET MESSAGE_TEXT = 'Order No not found in orders table'; END IF; -- more code below -- ... END
First, it counts the orders with the input order number that we pass to the stored procedure.
Second, if the number of order is not 1, it raises an error with SQLSTATE 45000 along with an error message saying that order number does not exist in the orders table.
Notice that 45000 is a generic SQLSTATE value that illustrates an unhandled user-defined exception.
If we call the stored procedure AddOrderItem() and pass a nonexistent order number, we will get an error message.
CALL AddOrderItem(10,'S10_1678',1,95.7,1);
MySQL RESIGNAL statement
Besides the SIGNAL statement, MySQL also provides the RESIGNAL statement that is used to raise a warning or error condition.
The RESIGNAL statement is similar to SIGNAL statement in term of functionality and syntax, except that:
You must use the
RESIGNALstatement within an error or warning handler, otherwise you will get an error message saying that “RESIGNAL when handler is not active”. Notice that you can useSIGNALstatement anywhere inside a stored procedure.You can omit all attributes of the
RESIGNALstatement, even theSQLSTATEvalue.
If you use the RESIGNAL statement alone, all attributes are the same as the ones passed to the condition handler.
The following stored procedure changes the error message before issuing it to the caller.
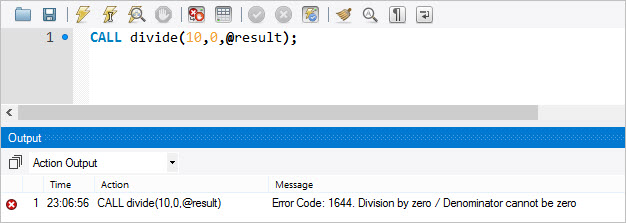
DELIMITER $$ CREATE PROCEDURE Divide(IN numerator INT, IN denominator INT, OUT result double) BEGIN DECLARE division_by_zero CONDITION FOR SQLSTATE '22012'; DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER FOR division_by_zero RESIGNAL SET MESSAGE_TEXT = 'Division by zero / Denominator cannot be zero'; -- IF denominator = 0 THEN SIGNAL division_by_zero; ELSE SET result := numerator / denominator; END IF; END
Let’s call the Divide() stored procedure.
CALL Divide(10,0,@result);
In this tutorial, we have shown you how to raise error conditions inside stored procedure using SIGNAL and RESIGNAL statements
原文链接:http://outofmemory.cn/mysql/procedure/mysql-signal-resignal
共同学习,写下你的评论
评论加载中...
作者其他优质文章