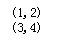-
1.对象指针:类名 * 指针名 = new 类名 2.C语言的malloc与C++的new都具有申请新内存空间的作用,但是new会调用对象的构造函数,而malloc不会调用 3. C++在new时的初始化的规律可能为:对于有构造函数的类,不论有没有括号,都用构造函数进行初始化;如果没有构造函数,则不加括号的new只分配内存空间,不进行内存的初始化,而加了括号的new会在分配内存的同时初始化为0。
查看全部 -
深拷贝实例
class Array { public: Array(int count); Array(const Array &arr); ~Array(); void setCount(int count); int getCount(); void printAddr(); void printArr(); private: int m_iCount; int *m_pArr; }; #include"Array.h" #include <iostream> using namespace std; Array::Array(int count) { m_iCount = count; m_pArr=new int[m_iCount]; for(int i=0;i<m_iCount;i++) { m_pArr[i]=i; } cout << "Array" <<endl; } Array::Array(const Array &arr) { m_iCount = arr.m_iCount; m_pArr =new int[m_iCount]; for(int i=0;i<m_iCount;i++) { m_pArr[i] = arr.m_pArr[i]; } cout <<"Array&" <<endl; } Array::~Array() { delete []m_pArr; m_pArr = NULL; cout <<"~Array" <<endl; } void Array::setCount(int count) { m_iCount = count; } int Array::getCount() { return m_iCount; } void Array::printAddr() { cout <<"m_pArr=" <<m_pArr <<endl; } void Array::printArr() { for(int i=0;i<m_iCount;i++) { cout << m_pArr[i] <<endl; } }
查看全部 -
class Array { public: Array(); Array(const Array &arr); ~Array(); void setCount(int count); int getCount(); private: int m_iCount; }; #include"Array.h" #include <iostream> using namespace std; Array::Array() { cout << "Array" <<endl; } Array::Array(const Array &arr) { m_iCount = arr.m_iCount; cout <<"Array&" <<endl; } Array::~Array() { cout <<"~Array" <<endl; } void Array::setCount(int count) { m_iCount = count; } int Array::getCount() { return m_iCount; } #include <iostream> #include <stdlib.h> #include "Array.h" using namespace std; int main() { Array arr1; arr1.setCount(5); Array arr2(arr1); cout << "arr2.m_iCount="<<arr2.getCount() <<endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
查看全部 -
浅拷贝:
将对象内容简单拷贝,指针成员指向同一地址
深拷贝:
在堆中开辟一块新的地址,将原地址中的内容拷贝进去
查看全部 -
查看全部
-
因为初始化列表会比构造函数先执行,再因为Coordinate是Line的对象成员,会优先于Line执行构造函数,所以如果不把Coordinate的那两个对象放在初始化列表中进行初始化,将会导致Coordinnate的对象使用默认构造函数进行初始化,然后你又没有写默认的构造函数,所以会报错,不过如果你写了默认构造函数,会导致多出来两个对象。
查看全部 -
demo.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string>
#include"Line.h"
using namespace std;
/*对象成员
要求:
定义两个类:
坐标类:Coordinate
数据成员:m_iX和m_iY
成员函数:构造函数,析构函数,数据封装函数
线段类:Line
数据成员:点A m_coorA,点B m_coorB
成员函数:构造函数,析构函数,数据封装函数,信息打印函数*/
int main(void)
{
Line *p = new Line();
delete p;
p = NULL;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
Line.cpp
#include"Line.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
Line::Line()
{
cout << "Line" << endl;
}
Line::~Line()
{
cout << "~Line" << endl;
}
void Line::setA(int x, int y)
{
m_coorA.setX(x);
m_coorA.setY(y);
}
void Line::setB(int x, int y)
{
m_coorB.setX(x);
m_coorB.setY(y);
}
void Line::printInfo()
{
cout << "(" << m_coorA.getX() << m_coorA.getY() << ")" << endl;
cout << "(" << m_coorB.getX() << m_coorB.getY() << ")" << endl;
}
Line.h#include"Coordinate.h"
class Line
{
public:
Line();
~Line();
void setA(int x,int y);
void setB(int x,int y);
void printInfo();
private:
Coordinate m_coorA;
Coordinate m_coorB;
};
Coordinate.cpp
#include"Coordinate.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
Coordinate::Coordinate()
{
cout << "Coordinate()" << endl;
}
Coordinate::~Coordinate()
{
cout << "~Coordinate()" << endl;
}
void Coordinate::setX(int x)
{
m_iX = x;
}
int Coordinate::getX()
{
return m_iX;
}
void Coordinate::setY(int y)
{
m_iY = y;
}
int Coordinate::getY()
{
return m_iY;
}
Coordinate.h
class Coordinate
{
public:
Coordinate();
~Coordinate();
void setX(int x);
int getX();
void setY(int y);
int getY();
private:
int m_iX;
int m_iY;
};
查看全部 -
对象成员:一个对象中包含其他对象 如:class Line{ public: Line(); private: Coordinate m_coorA; Coordinate m_coorB; } 当实例化这样一个对象时,会先实例化m_coorA,再实例化m_coorB,最后实例化Line 对象消亡时,会先销毁Line,再m_coorB,最后m_coorA
查看全部 -
栈中内存被销毁是在整个main函数执行完后销毁; 而堆中由指针P所指向的内存是可手动控制何时销毁(利用delete )可通过此来显示析构函数的存在;
查看全部 -
p[0]指向第一个元素;执行p++之后p[0]指向第2个了!!!<br>
2.释放内存时要注意指针 p 指回原来的位置。用delete释放数组内存时要注意此时的指针*p要指到该数组的第一个元素上。保证申请和释放的是同一段内存第二个循环第一次打印的是第三个元素因为指针经过p++到第三个元素了,所以得用p--
注意:在对象数组中,想要访问某个堆中的对象的成员属性时,p->m_ix=1;和p[0].m_ix=1效果是一样的,但是p[0]->m_ix=1这种用法是错误、以及注意 p++后 p[0] 前后的指向是不一样的
数组的头指针最好要保留,采用(p+1)->m_iX的方式访问,不会更改头指针
查看全部 -
首先,能用拍p[2]->m_iY=20 给第三个赋值吗? 是不不不可以的!!!! 还有,对于它——[],下标运算符,是这样处理的:p[2]等价于*(p+2),代表第三个元素实体本身. 而 -> 这个运算符是与指针(即地址)搭配使用的。即(p+2)->m_iY=20,是可以滴。 其实,对于学过的数组,a[i]那啥的,也是这样处理的:*(a+i),不过a代表数组名,是个常量而已。
查看全部 -
C++路线: 起航-->离港-->封装-->继承
查看全部 -
#include <iostream> #include <Windows.h> #include <string> #include <process.h> #include <Windows.h> using namespace std; /* https://zhidao.baidu.com/question/1755742141667975828.html 设定初始面向 East ( 如果是右手抹墙则是 West) 本代码以右手摸墙为例。 1如果当前格为第一排,则说明当前格为终点,结束。 2根据当前格的数据,找到下一步需要面向的方向, 方法是,如果当前方向上有墙,则逆时针(左手抹墙则顺时针)转身,重复这一步骤直到面向的方向上可以行走 3沿当前方向走一步 4顺时针(左手抹墙则逆时针)转身一次,使当前面对方向为第3步之后的游手(或左手)方向, 然后回到步骤1 [这样每走一步之后转身一次,是为了保证摸墙可以一直靠着墙走,这个方式非常好,就不用去每次判断你的右手边是不是有路, 因为每走一步之后你都向右转,这样你之前的右方就变成了前方,你只需要判断前方有没有路!!] */ //墙体和路常量 #define WALL "■" #define ROAD " " //迷宫大小常量 const int X = 8; const int Y = 8; //方向枚举 enum direction{ N = 0, S = 1, W = 2, E = 3 }; //地图类 class MazeMap { public: MazeMap() {} void coutMap(string map[X][Y]) { //构造地图 for (int i = 0; i < X; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < Y; j++) { cout << map[i][j] ; } cout << endl; } } }; //人类类 class Human { public: Human(string _man) :x(6), y(6), man_signal(_man), direction(W){} //初始化人物位置和图标 //横纵坐标 int x; int y; //人物显示标识 string man_signal; //方向 int direction; // 移动方法 void humanMove(string map[X][Y], Human *man) { MazeMap *mazeMap = new MazeMap; map[man->x][man->y] = man->man_signal; mazeMap->coutMap(map); cout << "READY?(y/n)" << endl; char flag = 'n'; cin >> flag; //单向寻路原则 右手摸墙,初始朝向为W if (flag == 'y') { do { turnLeft(map, man); move(map, man); Sleep(1000); system("cls");//清屏作用,动画的移动靠每一次一帧一帧的画面来实现。 mazeMap->coutMap(map);//清屏之后重绘迷宫,动画的移动靠每一次一帧一帧的画面来实现。 } while (finsh(man)); cout << "YOU WIN!!!" << endl; } else { cout << "YOU ARE A LOSE!!!" << endl; } delete mazeMap; mazeMap = NULL; } //右手摸墙原则: 如果正前方方向上有墙就逆时针转一下(向左转90°) void turnLeft(string map[X][Y],Human *man) { if (man->direction == N) { if (map[man->x - 1][man->y] == WALL) { man->direction = W; turnLeft(map, man);//循环,不停的左转直到找到前方不是墙 } return; } if (man->direction == S) { if (map[man->x+1][man->y] == WALL) { man->direction = E; turnLeft(map, man);//循环,不停的左转直到找到前方不是墙 } return; } if (man->direction == W) { if (map[man->x][man->y-1] == WALL) { man->direction = S; turnLeft(map, man);//循环,不停的左转直到找到前方不是墙 } return; } if (man->direction == E) { if (map[man->x][man->y+1] == WALL) { man->direction = N; turnLeft(map, man);//循环,不停的左转直到找到前方不是墙 } return; } } //移动一格 后顺时针调转方向(每次向前走一步之后,都把方向右转90° 为了保证右手摸墙原则,每次都往右边靠) void move(string map[X][Y], Human *man) { if (man->direction == N) { map[man->x - 1][man->y] = man->man_signal; map[man->x][man->y] = ROAD; man->x -= 1; man->direction = E; }else if (man->direction == S) { map[man->x + 1][man->y] = man->man_signal; map[man->x][man->y] = ROAD; man->x += 1; man->direction = W; }else if (man->direction == W) { map[man->x][man->y - 1] = man->man_signal; map[man->x][man->y] = ROAD; man->y -= 1; man->direction = N; }else if(man->direction == E) { map[man->x][man->y + 1] = man->man_signal; map[man->x][man->y] = ROAD; man->y += 1; man->direction = S; } return; } //判断是否完成 bool finsh(Human *man) { if (man->x == 0) return false; return true; } }; int main(void) { string map[X][Y] = { {WALL,ROAD,WALL,WALL,WALL,WALL,WALL,WALL}, {WALL,ROAD,ROAD,ROAD,ROAD,ROAD,WALL,WALL}, {WALL,WALL,WALL,WALL,WALL,ROAD,ROAD,WALL}, {WALL,ROAD,ROAD,ROAD,ROAD,ROAD,WALL,WALL}, {WALL,WALL,ROAD,WALL,ROAD,ROAD,WALL,WALL}, {WALL,WALL,ROAD,ROAD,ROAD,WALL,WALL,WALL}, {WALL,WALL,WALL,WALL,ROAD,ROAD,ROAD,WALL}, {WALL,WALL,WALL,WALL,WALL,WALL,WALL,WALL} }; Human *man = new Human("⊙"); man->humanMove(map,man); delete man; man = NULL; return 0; }查看全部 -
结构里面有指针,只拷贝了指针一个道理。
在C++里面还发明一个两个概念,深浅拷贝。
查看全部 -
一个对象的里面的对象成员的销毁顺序:先构建的后销毁。类似于栈
查看全部
举报