概述
本文是基于jdk8_271版本进行分析的。
Hashtable与HashMap一样,是一个存储key-value的双列集合。底层是基于数组+链表实现的,没有红黑树结构。Hashtable默认初始化容量为11,Hashtable也会动态扩容,与HashMap不同的是,每次扩容的容量是原容量2倍+1。Hashtable的key和value都不允许为null。Hashtable在方法上都加了synchronized同步锁。所以Hashtable是线程安全的,同时Hashtable的效率也相对较低。
数据结构
-
实现继承关系
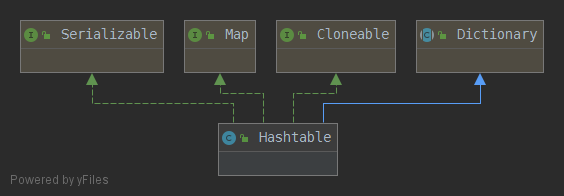
1 public class Hashtable<K,V>
2 extends Dictionary<K,V>
3 implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
- Dictionary:
- Map:
- Cloneable:
- Serializable:
-
成员变量
1 // 存放hash表数据
2 private transient Entry<?,?>[] table;
3
4 // 元素数量
5 private transient int count; 6
7 // 阈值。元素数量达到该值,进行扩容
8 private int threshold; 9
10 // 加载因子,默认是0.75
11 private float loadFactor; 12
13 // 修改次数
14 private transient int modCount = 0;
-
构造函数
Hashtable默认初始化容量为11,默认加载因子的值为0.75(与HashMap一样)。选择0.75作为默认的加载因子,完全是时间和空间成本上寻求的一种折中选择。加载因子过高虽然减少了空间开销,但同时也增加了查询成本;加载因子过低虽然可以减少查询时间成本,但是空间利用率很低。
Hashtable初始化容量值使用传入的值(0除外),不会重新计算(HashMap需要重新计算,使得容量大小为2的指数次幂)。在构造方法创建对象时,会直接初始化数组,没有采用懒加载的方式。
1 public Hashtable(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { 2 if (initialCapacity < 0)
3 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
4 initialCapacity);
5 if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) 6 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Load: "+loadFactor);
7 // 如果初始化容量传入的是0,则默认使用1
8 if (initialCapacity==0)
9 initialCapacity = 1; 10 this.loadFactor = loadFactor; 11 table = new Entry<?,?>[initialCapacity]; 12 // 计算阈值。预计的阈值为初始化容量*加载因子,预计的阈值如果大于MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1,则实际阈值设置为MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1
13 threshold = (int)Math.min(initialCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1); 14 } 15
16 public Hashtable(int initialCapacity) { 17 // 传入初始化容量,加载因子使用默认值0.75。初始化容量传入的是多少就初始化多大(0除外;传入的如果0,默认使用1),不需要再重新计算
18 this(initialCapacity, 0.75f); 19 } 20
21 public Hashtable() { 22 // 默认初始化容量11,默认加载因子0.75
23 this(11, 0.75f); 24 } 25
26 public Hashtable(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> t) { 27 // 初始化容量为传入集合元素数量的2倍(至少为11),加载因子使用默认值0.75
28 this(Math.max(2*t.size(), 11), 0.75f); 29 putAll(t); 30 }
主要方法解析
-
扩容方法
这里与HashMap扩容时候有点区别,链表数据迁移时候,Hashtable是在链表头部插入(和之前链表反过来),HashMap是在尾部插入。
1 protected void rehash() { 2 int oldCapacity = table.length; // 原容量值
3 Entry<?,?>[] oldMap = table; // 原数组 4
5 // overflow-conscious code
6 int newCapacity = (oldCapacity << 1) + 1; // 预计扩容的容量为原容量的2倍+1
7 if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) {
8 if (oldCapacity == MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) // 预计扩容容量如果大于容量最大值,并且原容量为容量最大值,则不进行扩容处理 9 // Keep running with MAX_ARRAY_SIZE buckets
10 return; 11 newCapacity = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; // 预计扩容容量如果大于容量最大值,则将新容量设置为容量最大值
12 } 13 Entry<?,?>[] newMap = new Entry<?,?>[newCapacity]; // 构建一个新数组
14
15 modCount++; // 修改次数+1 16 // 计算阈值。新容量值*加载因子,与容量最大值+1,两个比较取最小值
17 threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1); 18 table = newMap; 19
20 for (int i = oldCapacity ; i-- > 0 ;) { 21 // 遍历原数组,从后往前
22 for (Entry<K,V> old = (Entry<K,V>)oldMap[i] ; old != null ; ) { 23 // 遍历该索引位链表,这里与jdk8中hashmap有点区别,这里是在链表头部插入(和之前链表会反过来),hashmap是在尾部插入
24 Entry<K,V> e = old; 25 old = old.next; 26
27 int index = (e.hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % newCapacity; 28 e.next = (Entry<K,V>)newMap[index]; 29 newMap[index] = e; 30 } 31 } 32 }
-
添加元素
添加元素时,Hashtable与HashMap有3点区别:
- Hashtable的key-value都不允许为null。
- Hashtable是在链表头部插入(和之前链表反过来),HashMap是在尾部插入。
- Hashtable是先判断是否需要扩容,再插入元素;jdk8HashMap是先插入元素再判断是否需要扩容。
1 public synchronized V put(K key, V value) { 2 // Make sure the value is not null
3 if (value == null) {
4 // value为空,会抛出空指针异常
5 throw new NullPointerException(); 6 }
7
8 // Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
9 Entry<?,?> tab[] = table; 10 int hash = key.hashCode(); 11 int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length; 12 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 13 Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index]; 14 for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) { 15 if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) { 16 // 该key已经存在,直接替换原值
17 V old = entry.value; 18 entry.value = value; 19 return old; 20 } 21 } 22 // 添加元素
23 addEntry(hash, key, value, index); 24 return null; 25 } 26 private void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int index) { 27 modCount++; 28
29 Entry<?,?> tab[] = table; 30 if (count >= threshold) { // 判断是否元素数量是否达到阈值,如果达到先进行扩容处理 31 // Rehash the table if the threshold is exceeded
32 rehash(); 33
34 tab = table; 35 hash = key.hashCode(); 36 index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length; 37 } 38
39 // Creates the new entry.
40 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 41 Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>) tab[index]; 42 // 插入元素是在链表头部插入
43 tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e); 44 count++; 45 }
-
删除元素
1 public synchronized V remove(Object key) { 2 Entry<?,?> tab[] = table; 3 int hash = key.hashCode(); 4 int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length; 5 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
6 Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
7 for(Entry<K,V> prev = null ; e != null ; prev = e, e = e.next) { 8 if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) { 9 modCount++; 10 if (prev != null) { 11 prev.next = e.next; 12 } else { 13 tab[index] = e.next; 14 } 15 count--; 16 V oldValue = e.value; 17 e.value = null; 18 return oldValue; 19 } 20 } 21 return null; 22 } 23 public synchronized boolean remove(Object key, Object value) { 24 Objects.requireNonNull(value); 25
26 Entry<?,?> tab[] = table; 27 int hash = key.hashCode(); 28 int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length; 29 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 30 Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index]; 31 for (Entry<K,V> prev = null; e != null; prev = e, e = e.next) { 32 if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key) && e.value.equals(value)) { 33 modCount++; 34 if (prev != null) { 35 prev.next = e.next; 36 } else { 37 tab[index] = e.next; 38 } 39 count--; 40 e.value = null; 41 return true; 42 } 43 } 44 return false; 45 }
-
序列化/反序列化方法
1 private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) 2 throws IOException { 3 Entry<Object, Object> entryStack = null;
4
5 synchronized (this) {
6 // Write out the threshold and loadFactor
7 s.defaultWriteObject();
8
9 // Write out the length and count of elements
10 s.writeInt(table.length); 11 s.writeInt(count); 12
13 // Stack copies of the entries in the table
14 for (int index = 0; index < table.length; index++) { 15 Entry<?,?> entry = table[index]; 16
17 while (entry != null) { 18 entryStack =
19 new Entry<>(0, entry.key, entry.value, entryStack); 20 entry = entry.next; 21 } 22 } 23 } 24
25 // Write out the key/value objects from the stacked entries
26 while (entryStack != null) { 27 s.writeObject(entryStack.key); 28 s.writeObject(entryStack.value); 29 entryStack = entryStack.next; 30 } 31 } 32
33 private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) 34 throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException 35 { 36 // Read in the threshold and loadFactor
37 s.defaultReadObject(); 38
39 // Validate loadFactor (ignore threshold - it will be re-computed)
40 if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) 41 throw new StreamCorruptedException("Illegal Load: " + loadFactor); 42
43 // Read the original length of the array and number of elements
44 int origlength = s.readInt(); 45 int elements = s.readInt(); 46
47 // Validate # of elements
48 if (elements < 0) 49 throw new StreamCorruptedException("Illegal # of Elements: " + elements); 50
51 // Clamp original length to be more than elements / loadFactor 52 // (this is the invariant enforced with auto-growth)
53 origlength = Math.max(origlength, (int)(elements / loadFactor) + 1); 54
55 // Compute new length with a bit of room 5% + 3 to grow but 56 // no larger than the clamped original length. Make the length 57 // odd if it's large enough, this helps distribute the entries. 58 // Guard against the length ending up zero, that's not valid.
59 int length = (int)((elements + elements / 20) / loadFactor) + 3; 60 if (length > elements && (length & 1) == 0) 61 length--; 62 length = Math.min(length, origlength); 63
64 if (length < 0) { // overflow
65 length = origlength; 66 } 67
68 // Check Map.Entry[].class since it's the nearest public type to 69 // what we're actually creating.
70 SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess().checkArray(s, Map.Entry[].class, length); 71 table = new Entry<?,?>[length]; 72 threshold = (int)Math.min(length * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1); 73 count = 0; 74
75 // Read the number of elements and then all the key/value objects
76 for (; elements > 0; elements--) { 77 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 78 K key = (K)s.readObject(); 79 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 80 V value = (V)s.readObject(); 81 // sync is eliminated for performance
82 reconstitutionPut(table, key, value); 83 } 84 }
作者: Yanci丶
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/Y2EX/p/14804679.html
共同学习,写下你的评论
评论加载中...
作者其他优质文章