-
二叉树的三种遍历方式:
- 前序遍历:根-左节点-右节点
- 中序遍历:左节点-根-右
- 后序遍历:左-右-根
查看全部 -
前序遍历:根左右:根>根(左)>左>右(左)>根(右)>左(右)>右
中序遍历:左根右:左>根(左)>右(左)>根>左(右)>根(右)>右
后序遍历:左右根:左>右(左)>根(左)>左(右)>右>根(右)>根
查看全部 -
对于数组表示的二叉树:简单遍历,无前中后序
函数:
创造函数和析构函数——创建和销毁树
SearchNode(Tree *pTree,int nodeIndex):搜索节点,要指定数组下标
AddNode(Tree *pTree,int nodeIndex,int direction,Node *pNode):指定往哪一个下标的节点上去添加节点;指定方向:添加的是左孩子还是右孩子;指定要添加的节点:把要添加的节点挂在指定的位置上(相对于根节点而言)
查看全部 -
树的节点的搜索:指定当前节点的索引(下标)即可找到对应的数据
查看全部 -
完全可以把一个数组看作一个二叉树
一个节点若只有右子树而没有左子树,则用 0表达当前位置不存在节点的情况。
索引是与数组与生俱来的。
对于父节点来说,其下标*2+1:左孩子 ; 其下标*2+2:右孩子
查看全部 -
树的用途:
压缩软件--赫夫曼树
搜索--人机对战
查看全部 -
二叉树:
1、所有结点的度都小于等于2
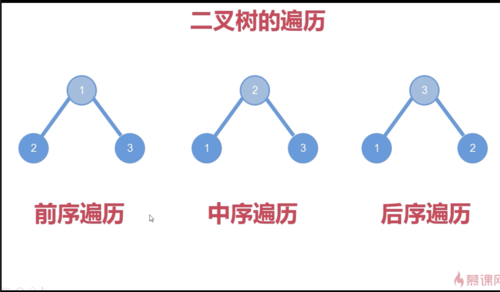
二叉树的遍历:( 相对于二叉树的根来说)
前序遍历:先访问根,再访问左右节点--根左右
中序遍历:先访问左节点,再访问根,再访问右节点--左根右
后序遍历:先访问左右节点,再访问根(访问根的操作在最后)--左右根
查看全部 -
树是节点的有限集合
每一个元素都是一个节点
根节点:双亲(一个节点,父节点)
度:当前节点的直接孩子个数
A接着三个节点,度为3,BCD的双亲就是A 节点,A 的孩子就是BCD
对于一棵树来说,终端节点:叶子(EFGHC);非终端节点根:(相对于叶子来说)
有序树:节点不可换顺序;无序树:节点可换顺序而不影响逻辑
祖先:当前节点向上的节点直至总根均为其祖先;子孙:从该节点向下伸出的连接的节点均属于其子孙(A的子孙为BCDEFGH)
深度:结点深度&树的深度
结点深度:与所在层数有关,在第几层深度就为几;
树的深度:当前树中结点所具有的最大深度
森林:多颗独立的树放在一起成为森林;也可孤木成林
查看全部 -
树
二叉树的遍历分为前序,中序,后续
前中后是访问根节点顺序分为前中后而定义
查看全部 -
发现一个学it不错的网站 百度搜索 it猿课 网址 http://ityuanke.com 里面好像市面全部课都有查看全部
-
发现一个学it不错的网站 百度搜索 it猿课 网址 http://ityuanke.com 里面好像市面全部课都有查看全部
-
按照树的结构遍历输出:
 查看全部
查看全部 -
递归删除子节点
 查看全部
查看全部 -
关于树的遍历,在递归中,一直往下层走,是如何返回上一层的?
cout << this->Index << endl; //先输出当前结点。
this->pLchild->ProTraversal(); //在左结点中,先输出左结点,如果没有左右结点,结束语句(跳出函数)。
this->pRchild->ProTraversal(); //在右结点中,先输出右结点,如果没有左右结点,结束语句(跳出函数)。
函数有执行顺序的,先执行最最最里层的函数,再跳出该函数继续执行倒第二层函数接下来的函数。以此类推,最后一次执行的是第一次调用此函数的return。
查看全部 -
用数组表达二叉树。 没有节点的地方用0表示。父节点下标*2+1 表示左孩子。 父节点下标*2+2表示右孩子
我们在构建树的时候一般都不会用数组,因为我们一开始不会知道树有多少个节点,用数组的话我们是一开始就声明一段连续的内存,如果节点没有预设的那么多就会浪费内存;如果节点超出预计数量,就要重新建立一个新的数组把原来数组的数据传去新的数组,这样会浪费计算资源。用指针的话方便无限添加新节点,用数组建构的树,节点与节点之间不需要是连续的内存,只需要在建立新节点的时候把指针指向父节点即可,方便对树进行添加与删除的操作。
查看全部 -
二叉树的遍历,前中后是相对于根节点来说的。先访问根节点就是前序,以此类推
查看全部 -
二叉树就是所有节点的度<=2的树
查看全部 -
树是节点的有限集合
查看全部 -
Node.cpp中的SearchNode(int nodeIndex)函数可以很简化,如下:
Node* Node::SearchNode(int nodeIndex)
{
if (this->index == nodeIndex)
return this;
if (this->pLChild != NULL)
if (this->pLChild->SearchNode(nodeIndex) != NULL)
return this->pLChild->SearchNode(nodeIndex);
if (this->pRChild != NULL)
return this->pRChild->SearchNode(nodeIndex);
return NULL;
}
查看全部 -
main.cpp: #include <iostream> #include "Tree.h" #include <stdlib.h> using namespace std; /* 二叉树(用链表表达) 结点要素:索引 数据 左孩子指针 右孩子指针 父结点指针 (头节点的父结点指针为NULL,叶结点的左右孩子结点指针为NULL) 索引: 数组表达的二叉树中的索引指的就是数组的下标 链表表达时,索引必须也是当前结点的一部分,所以需要用一个数据成元来表示索引 int tree[n] 3 5 8 2 6 9 7 数据: 此处用int 左孩子指针、右孩子指针:拿到一个结点时,可以通过其左孩子指针、右孩子指针分别访问其左孩子结点、右。 (0) 5(1) 8(2) 2(3) 6(4) 9(5)7(6) 前序遍历:(下标)0 1 3 4 2 5 6 中序遍历: 3140526 后序遍历:3415620 如果要在孩子结点挂载孩子,需要通过搜索找到孩子结点的索引,所以,查找结点是一个基本操作,通过头结点找到结点,再进行其他操作。 如果要删除结点,不仅删除一个结点,需要把其所有子结点和子结点的子结点全部删除 销毁树时,也需要通过指针一级一级地找到头结点一下的所有结点一一进行消除,否则造成内存的泄漏 */ int main() { Node *node1 = new Node(); node1->index = 1; node1->data = 5; Node *node2 = new Node(); node2->index = 2; node2->data = 8; Node *node3 = new Node(); node3->index = 3; node3->data = 2; Node *node4 = new Node(); node4->index = 4; node4->data = 6; Node *node5 = new Node(); node5->index = 5; node5->data = 9; Node *node6 = new Node(); node6->index = 6; node6->data = 7; Tree *tree = new Tree(); tree->AddNode(0,0,node1); tree->AddNode(0,1,node2); tree->AddNode(1,0,node3); tree->AddNode(1,1,node4); tree->AddNode(2,0,node5); tree->AddNode(2,1,node6); // tree->PreorderTraversal(); tree->InorderTraversal(); // tree->PostorderTraversal(); return 0; }Tree.cpp: #include "Tree.h" #include "Node.h" #include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> using namespace std; Tree::Tree(){ m_pRoot = new Node();//头节点不放有意义的值,index为0; } Tree::~Tree() {//销毁树 DeleteNode(0,NULL); //或者m_pRoot->DeleteNode(); } Node *Tree::SearchNode(int nodeIndex) {//根据索引寻找结点 //递归函数 return m_pRoot->SearchNode(nodeIndex); } bool Tree::AddNode(int nodeIndex,int direction,Node *pNode) {//添加结点 Node *temp = SearchNode(nodeIndex); if(temp == NULL){ return false;//根本没有找到对应结点 } //不能直接用外面传进来的结点,因为外面的函数可以对其进行修改,容易导致其他错误 Node *node = new Node(); if(node == NULL){ return false; } //只需要对这两个值进行复制,其他三个指针不用,因为三个指针的值取决于结点在树中的位置 node->index = pNode->index; node->data = pNode->data; node->pParent = temp; if(direction == 0){ temp->pLChild = node; } if(direction == 1){ temp->pRChild = node; } return true; } bool Tree::DeleteNode(int nodeIndex,Node *pNode) {//删除结点 Node *temp = SearchNode(nodeIndex); if(temp == NULL){ return false;//根本没有找到对应结点 } if(pNode != NULL){//若pNode==NULL,意思就是不要这个结点,删了不需要 pNode->data = temp->data; } //删除结点在树这个层面不太容易操作,所以在Node级进行操作 //对于Node来说,删除自己需要: // 1.把自己的子结点删除 // 2.看自己是父结点的左孩子还是右孩子,把父结点对应指针置为NULL,然后再自杀; temp->DeleteNode(); return true; } void Tree::PreorderTraversal() {//前序遍历,在Node中比在Tree中更容易实现 m_pRoot->PreorderTraversal(); } void Tree::InorderTraversal() {//中序遍历 m_pRoot->InorderTraversal(); } void Tree::PostorderTraversal() {//后序遍历 m_pRoot->PreorderTraversal(); }Tree.h: #ifndef INC_0210_TREE_H #define INC_0210_TREE_H #include "Node.h" #include <stdio.h> class Tree{ public: Tree();//创建树 ~Tree();//销毁树 Node *SearchNode(int nodeIndex);//根据索引寻找结点 bool AddNode(int nodeIndex,int direction,Node *pNode);//添加结点 bool DeleteNode(int nodeIndex,Node *pNode);//删除结点 void PreorderTraversal();//前序遍历 void InorderTraversal();//中序遍历 void PostorderTraversal();//后序遍历 private: Node *m_pRoot; }; #endif //INC_0210_TREE_HNode.h: #include <stdio.h> #ifndef INC_0210_NODE_H #define INC_0210_NODE_H class Node{ public: Node(); Node *SearchNode(int nodeIndex); void DeleteNode(); void PreorderTraversal();//前序遍历 void InorderTraversal();//中序遍历 void PostorderTraversal();//后序遍历 //需要注意,bool不需要,因为在树这个类中已经找到结点类,无所谓找得到与否,所以也不需要nodeIndex。 //第二个参数也不需要了,在Tree中的删除函数已经取到了 int index; int data; Node *pLChild; Node *pRChild; Node *pParent; }; #endif //INC_0210_NODE_HNode.cpp: #include "Node.h" #include "Tree.h" #include <stdio.h> #include <iostream> using namespace std; Node::Node() { index = 0; data = 0; pLChild = NULL; pRChild = NULL; pParent = NULL; } Node *Node::SearchNode(int nodeIndex){//一个是Tree下面的SearchNode,一个是Node下面的SearchNode,功能基本相同 //在Node下面实现这个功能,这个功能将来被Tree这个类调用 if(this->index == nodeIndex){ return this;//返回当前这个结点 } Node *temp = NULL; if(this->pLChild != NULL){ if(this->pLChild->index == nodeIndex){ return this->pLChild; } //若不是左孩子 else{ temp = this->pLChild->SearchNode(nodeIndex); if(temp != NULL) return temp; } } if(this->pRChild != NULL){ if(this->pRChild->index ==nodeIndex){ return this->pRChild; } else{ temp = this->pRChild->SearchNode(nodeIndex); if(temp != NULL) return temp; } } return NULL; } void Node::DeleteNode() { if(this->pLChild != NULL){ this->pLChild->DeleteNode(); } if(this->pRChild != NULL){ this->pRChild->DeleteNode(); } if(this->pParent != NULL){ if(this->pParent->pLChild == this){ this->pParent->pLChild = NULL; } if(this->pParent->pRChild == this){ this->pParent->pRChild = NULL; } } delete this; } void Node::PreorderTraversal() {//前序遍历,在Node中比在Tree中更容易实现 cout << this->index << " "<< this->data << endl; if(this->pLChild != NULL){ this->pLChild->PreorderTraversal();//通过递归,将访问左结点的概念变成访问左子树 } if(this->pRChild != NULL){ this->pRChild->PreorderTraversal(); } } void Node::InorderTraversal() {//中序遍历 if(this->pLChild != NULL){ this->pLChild->InorderTraversal(); } cout << this->index << " "<< this->data << endl; if(this->pRChild != NULL){ this->pRChild->InorderTraversal(); } } void Node::PostorderTraversal() {//后序遍历 if(this->pLChild != NULL){ this->pLChild->PostorderTraversal(); } if(this->pRChild != NULL){ this->pRChild->PostorderTraversal(); } cout << this->index << " "<< this->data << endl; }查看全部 -
数组表示二叉树:
Tree.h: #ifndef INC_0210_TREE_H #define INC_0210_TREE_H class Tree{ public: Tree(int size,int *pRoot);//创建树 ~Tree();//销毁树 int *SearchNode(int nodeIndex);//根据索引寻找结点 bool AddNode(int nodeIndex,int direction,int *pNode);//添加结点 bool DeleteNode(int nodeIndex,int *pNode);//删除结点 void TreeTraverse();//遍历结点 private: int *m_pTree;//指针指向数组,数组在构造函数中去分配,在析构函数中去销毁 int m_iSize; }; #endif //INC_0210_TREE_HTree.cpp: #include "Tree.h" #include <iostream> using namespace std; Tree::Tree(int size,int *pRoot) { m_iSize = size; m_pTree = new int[size]; //初始化为0 for(int i =0;i < size ;i++){ m_pTree[i] = 0; } m_pTree[0] = *pRoot;//初始化根结点 } Tree::~Tree(){ delete []m_pTree; m_pTree = NULL; } int *Tree::SearchNode(int nodeIndex){ //对nodeIndex的合法性进行判断 if(nodeIndex < 0 || nodeIndex >= m_iSize){ return NULL; } //若当前结点没有意义 if(m_pTree[nodeIndex] == 0){ return NULL; } return &m_pTree[nodeIndex]; } bool Tree::AddNode(int nodeIndex,int direction,int *pNode){ //先找到对应结点,之前还是需要进行合法性判断 if(nodeIndex < 0 || nodeIndex >= m_iSize){ return false; } //若当前结点没有意义 if(m_pTree[nodeIndex] == 0){ return false; } //若合法,0-左,1-右 if(direction == 0){ if( nodeIndex * 2 + 1 >= m_iSize){ return false; } //若当前结点没有意义 if(m_pTree[nodeIndex * 2 + 1] != 0){//若左节点已经有值 return false; } m_pTree[nodeIndex * 2 + 1] = *pNode;//pNode本身是一个指针,我们需要往里面放内容 } if(direction == 1){ if( nodeIndex * 2 + 2 >= m_iSize){ return false; } //若当前结点没有意义 if(m_pTree[nodeIndex * 2 + 2] != 0){//若左节点已经有值 return false; } m_pTree[nodeIndex * 2 + 2] = *pNode;//pNode本身是一个指针,我们需要往里面放内容 } return true; } bool Tree::DeleteNode(int nodeIndex,int *pNode){ //先找到对应结点,之前还是需要进行合法性判断 if(nodeIndex < 0 || nodeIndex >= m_iSize){ return false; } //若当前结点没有意义 if(m_pTree[nodeIndex] == 0){ return false; } //若合法,则传出来 *pNode = m_pTree[nodeIndex]; //然后把对应结点删除,即置零 m_pTree[nodeIndex] = 0; return true; } void Tree::TreeTraverse(){ for(int i=0;i<m_iSize;i++){ cout << m_pTree[i]<<" "; } }main.cpp: #include <iostream> #include "Tree.h" #include <stdlib.h> using namespace std; /* 二叉树(数组表示,也可以使用链表表达) 课程要求:完成树的基本操作 1.树的创建和销毁 2.树中节点的搜索 3.树中节点的添加与删除 4.树中节点的遍历 BOOL CreatTree(Tree **pTree,Node *pRoot);//创建树 void DestroyTree(Tree *pTree);//销毁树 Node *SearchNode(Tree *pTree,int nodeIndex);//根据索引寻找节点 BOOL AddNode(Tree *pTree,int nodeIndex,int direction,Node *pNode);//添加节点 BOOL DeleteNode(Tree *pTree,int nodeIndex,Node *pNode);//删除节点 void TreeTraverse(Tree *pTree);//遍历 关于数组与树之间的算法转换 int tree[n] 3 5 8 2 6 9 7 3(0) 父结点下标*2+1 该结点左 父结点下标*2+2 该结点右 5(1) 8(2) 2(3) 6(4) 9(5)7(6) */ int main() { int root = 3; Tree *pTree = new Tree(10,&root);//调用构造函数 int node1 = 5; int node2 = 8; pTree->AddNode(0,0,&node1); pTree->AddNode(0,1,&node2); int node3 = 2; int node4 = 6; pTree->AddNode(1,0,&node3); pTree->AddNode(1,1,&node4); int node5 = 9; int node6 = 7; pTree->AddNode(2,0,&node5); pTree->AddNode(2,1,&node6); int node = 0; pTree->DeleteNode(6,&node); cout <<endl <<"node="<<node<< endl; pTree->TreeTraverse(); int *p = pTree->SearchNode(2); cout <<endl <<"node="<< *p << endl; delete pTree;//调用析构函数 return 0; }查看全部 -
树是节点的有限集合
度:当前节点的直接的孩子(子节点)
结点深度:在第几层深度就是几
树深度
二叉树
1.所有结点的度都<=2
2.(对于根来说)
树的用途:人机对战
查看全部 -
二叉树节点要素:
索引 数据 左孩子指针 右孩子指针 父节点指针
查看全部 -
之前的是数组二叉树
现在是链表二叉树
查看全部 -
数组2叉树 删除一个节点 该节点数据=0则可
查看全部 -
插入节点,只需要将索要插入的节点内容赋值给被插入的节点则可
查看全部 -
节点序列 根节点序列为n,则2n+1为根节点的左节点
查看全部
举报










