2 回答
TA贡献2011条经验 获得超2个赞
考虑使用单个字符串来格式化
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
A = [5,4,3]
fig, ((ax1, ax2, ax3), (ax4, ax5, ax6)) = plt.subplots(2, 3, figsize=(22,10), sharex='col', sharey='row')
plot1, = ax1.plot([0,1], linestyle='None', marker='o', color='#6E9EAF', markersize=5)
plot1_R, = ax1.plot([0,1], linewidth=2, color="orange")
ax1.legend([plot1_R],
["$f(x) = {m}*x +{b}$\n$R2 = {r}$".format(m=np.round(A[1],2),
b=np.round(A[0],2), r=np.round(A[2],2))])
plt.show()
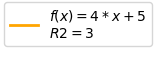
此外,f-strings 在这里可能会变得方便,其中在格式级别执行舍入。
ax1.legend([plot1_R], [f"$f(x) = {A[1]:.2f}*x +{A[0]:.2f}$\n$R2 = {A[2]:.2f}$"])
TA贡献1862条经验 获得超7个赞
在 python 中,你可以像这样连接字符串:
"hello " "world"
并产生"hello world". 但是如果你这样做,就会出现语法错误:
"{} ".format("hello") "world"
因此,如果您想从 的输出进行连接format(),请使用+:
"{} ".format("hello") + "world"
在你的情况下(为了可读性添加了换行符):
plt1.legend([plot1_R], [
"$f(x) = {m}*x +{b}$".format(m=np.round(A[1],2), b=np.round(A[0],2))
+ "\n"
+ "$R2 = {r}$".format(r=np.round(A[2],2))
])
添加回答
举报
