2 回答
TA贡献1833条经验 获得超4个赞
问:“Fargate/ECS/ZeroMQ 有什么我在这里缺少的吗???”
可能是,可能不是。
让我们以结构化的方式开始,深入了解根本原因:
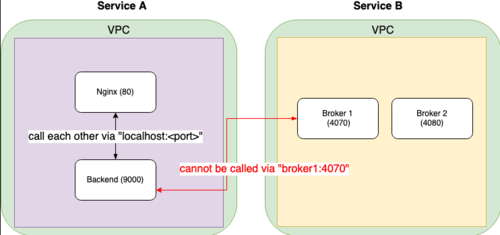
步骤 0:Broker服务节点
提到要使用 ZeroMQ,所以我们将从这一点开始。鉴于您的选择是使用 AccessPoint 到DEALERon address( *:4070 )和 AccessPoint to ROUTERon address ( *:4080 ),并且都使用.bind()-method 来激活-Microservice 节点tcp://内的 -Transport 类Broker,我们的下一步是验证该节点是否以及如何实际对世界其他地方可见。
所以,让它运行。
第 1 步:视线测试
这是测试的第一步Broker--Node,无论它的实现是什么,对“目标受众”实际上是可见的吗?如果没有,ZeroMQ 或其他框架内没有太多可做的,但您的任务是获取地址、L1 信号互连、L2-arp/rarp MAC-检测/映射、L3-路由权限/访问列表/filters/xlations/etc,(动态)DNS-updates 和所有其他配置更新,这样您就可以让世界其他地方的(选择性部分)看到并离成功更近一步.connect()
$ # is it L3-(in)-visible # a [ PASS ] | [ FAIL ]
$ ping <_a_Broker_Node_Assumed_TCP/IP_Address> # a [ PASS ] | [ FAIL ]
第 2 步:端口号 RTO-Test
$ # 4070 # a [ PASS ] | [ FAIL ]
$ netcat -vz <_a_Broker_Node_visible_TCP/IP_Address> 4070 # a [ PASS ] | [ FAIL ]
$ ######
$ # OR :
$ ######
$ telnet <_a_Broker_Node_visible_TCP/IP_Address> 4070 # a [ PASS ] | [ FAIL ]
Trying
Connected to
Escape character is '^]'.
https://<_a_Broker_Node_visible_TCP/IP_Address>:4070
HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
Server: nginx
Date: Mon, 03 May 2020 18:14:54 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 150
Connection: close
<html>
<head><title>400 Bad Request</title></head>
<body>
<center><h1>400 Bad Request</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx</center>
</body>
</html>
Connection closed by foreign host.
$
$ // 4080 // a [ PASS ] | [ FAIL ]
$ telnet <_a_Broker_Node_visible_TCP/IP_Address> 4080 // a [ PASS ] | [ FAIL ]
第 3 步:本地消息发送的 RTO 测试
替换相当复杂的REQ/ROUTER-Scalable Formal Communications Archetype Pattern 领域,让我们用一个简单的PUSH/PULL-message 传递测试进行测试,它(出于显而易见的原因)与发送消息的预期用途相匹配:
package main
import (
zmq "github.com/pebbe/zmq4"
"log"
"fmt"
"time"
...
)
func PushTASK() {
aCtx, err := zmq.NewContext()
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln( "__NACK: aCtx instantiation failed in zmq.NewContext()",
err )
}
aPusher, err := aCtx.NewSocket( zmq.PUSH )
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln( "__NACK: aPusher instantiation failed in aCtxNewSocket()",
err )
}
err = aPusher.SetLinger( 0 )
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln( "__NACK: aPusher instance failed to .SetLinger()",
err )
}
err = aPusher.SetConflate( true )
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln( "__NACK: aPusher instance failed to .SetConflate()",
err )
}
log.Println( "POSACK: aPusher instantiated and about to .connect( tcp://addr:port#)" )
err = aPusher.Connect( "tcp://broker:4070" )
if err != nil {
log.Print( fmt.Errorf( "__NACK: aPusher failed to .connect(): %w",
err )
)
}
log.Println( "POSACK: aPusher RTO and about to .SendMessage*()-loop" )
for aPush_NUMBER := 1; aPush_NUMBER < 10000; aPush_NUMBER++ {
err = aPusher.SendMessageDontwait( aPush_NUMBER )
if err != nil {
log.Print( fmt.Errorf( "__NACK: aPusher failed to .SendMessageDontwait()[%d]: %w",
aPush_NUMBER,
err )
)
}
time.Sleep( 0.1 * time.Second )
}
// ---------------------------------------------------BE NICE TO RESOURCES USED
err = aPusher.Disconnect( "tcp://broker:4070" )
if err != nil {
log.Print( fmt.Errorf( "__NACK: aPusher failed to .Disconnect( tcp://addr:port ): %w",
err )
)
}
// ---------------------------------------------------BE NICE TO RESOURCES USED
err = aPusher.Close()
if err != nil {
log.Print( fmt.Errorf( "__NACK: aPusher failed to .Close(): %w",
err )
)
}
// ---------------------------------------------------BE NICE TO RESOURCES USED
err = aCtx.Term()
if err != nil {
log.Print( fmt.Errorf( "__NACK: aCtx failed to .Term(): %w",
err )
)
}
// ---------------------------------------------------WE ARE CLEAR TO TERMINATE
}
第 4 步:远程消息接收的 RTO 测试
如果[ PASS ] | [ FAIL ]-tests 都没有崩溃,下一步是反映PUSH"remote" 的 -side 概念Broker,是的,重写它以使用PULL-side 并部署它以查看是否也没有崩溃以及是否消息在仍在运行或重新运行第 3 步时按应有的方式到达。
第 5 步:享受 ZeroMQ 的强大功能
一旦上述所有测试确实完成了[ PASS ],您不仅可以确定 ZeroMQ 不是阻碍因素,而且还可以将部署的原则增强到任何进一步的用例场景中,给定 L1-/L2-/L3-/ZeroMQ-服务以正确和可验证的方式落实到位。
- 2 回答
- 0 关注
- 211 浏览
添加回答
举报