1 回答
TA贡献1735条经验 获得超5个赞
这里有几个我不明白的问题:
无需在“拟合函数”中定义拟合函数
如果唯一的区别是字典的命名,则无需定义两次。(虽然我不明白为什么首先必须以不同的方式命名)
一个可以直接拟合频率而不是欧米茄
预先计算拟合值时,直接使用给定的fitfunction
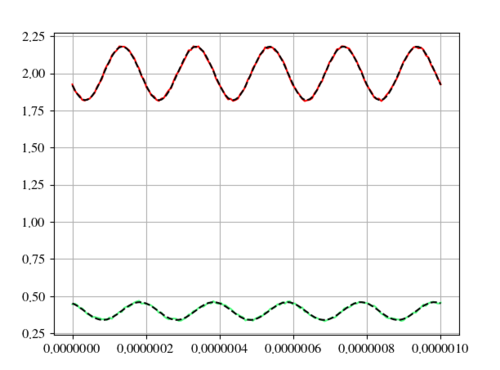
总的来说,我不明白为什么第二次拟合会失败并且在这里使用一些通用数据,但事实并非如此。考虑到物理学中幅度可能很复杂的事实,我对负面结果没有问题。不过,我理解 OP 中的要点。当然,拟合算法不了解物理学,从数学上讲,幅度为负是没有问题的。这只是给出了 pi 的额外相移。因此,在处理所需的相移时,可以很容易地强制施加正幅度。我在这里介绍了这个作为可能的关键字参数。此外,我将其简化为一个适合函数,并可能将输出字典键“重命名”为关键字参数。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from scipy.optimize import curve_fit
def sinfunc( t, A, f, p, c ):
return A * np.sin( 2.0 * np.pi * f * t + p) + c
def fit_sin(t_APD, y_APD, addName="", posamp=False):
''' Fit sin to the input time sequence, and return fitting parameters "amp", "omega", "phase", "offset", "freq", "period" and "fitfunc" '''
ff = np.fft.fftfreq( len( t_APD ), t_APD[1] - t_APD[0] ) # assume uniform spacing
Fyy = abs( np.fft.fft( y_APD ) )
guess_freq = abs( ff[np.argmax( Fyy[1:] ) + 1] ) # excluding the zero frequency "peak", which is related to offset
guess_amp = np.std( y_APD ) * 2.**0.5
guess_offset = np.mean( y_APD )
guess = np.array( [ guess_amp, guess_freq, 0., guess_offset ] )
popt, pcov = curve_fit(sinfunc, t_APD, y_APD, p0=guess, maxfev=500) # with maxfev= number I can increase the number of iterations
if popt[0] < 0 and posamp:
popt[0] = -popt[0]
popt[2] += np.pi
popt[2] = popt[2] % ( 2 * np.pi )
A, f, p, c = popt
fitted_APD = sinfunc( t_APD, *popt )
dic_APD = {
"amp{}".format(addName): A,
"omega{}".format(addName): 2.0 * np.pi * f,
"phase{}".format(addName): p,
"offset{}".format(addName): c,
"freq{}".format(addName): f,
"period{}".format(addName): 1.0 / f,
"fitfunc{}".format(addName): fitted_APD,
"maxcov{}".format(addName): np.max( pcov ),
"rawres{}".format(addName): ( guess, popt, pcov ) }
return dic_APD
tl = np.linspace(0,1e-6, 150 )
sl1 = np.fromiter( (sinfunc(t, .18, 4998735, 3.6, 2.0 ) + .01 *( 1 - 2 * np.random.random() ) for t in tl ), np.float )
sl2 = np.fromiter( (sinfunc(t, .06, 4998735, 2.1, 0.4 ) + .01 *( 1 - 2 * np.random.random() ) for t in tl ), np.float )
ld = fit_sin(tl, sl1, addName="_ld" )
print ld["amp_ld"]
ld = fit_sin(tl, sl1, addName="_ld", posamp=True )
print ld["amp_ld"]
apd = fit_sin(tl, sl2 )
fig = plt.figure("1")
ax = fig.add_subplot( 1, 1, 1 )
ax.plot( tl, sl1, color="r" )
ax.plot( tl, ld["fitfunc_ld"], color="k", ls="--" )
ax.plot( tl, sl2, color="#50FF80" )
ax.plot( tl, apd["fitfunc"], color="k", ls="--" )
ax.grid()
plt.show()
这给了我:
-0.180108427200549
0.180108427200549
即在第一次尝试中,尽管对幅度进行了很好的猜测,但结果为负。这可能是由于大相位。由于该猜测为零,因此算法更容易先切换幅度的符号,然后再调整相位。如上所述,这很容易纠正,甚至不需要错误传播。
添加回答
举报
