-
切片的半开半闭性质
查看全部 -
有三个长方体,他们的长宽高分别是[1, 2, 3], [5, 3, 2], [7, 3, 2],定义在数组L中,L = [[1, 2, 3], [5, 3, 2], [7, 3, 2]],请分别求出三个长方体的表面积。
?不会了怎么办
参考答案:
L = [[1,2,3], [5, 3, 2], [7,3,2]]
for cube in L:
length = cube[0]
width = cube[1]
height = cube[2]
result = length * width * 2 + width * height * 2 + length * height * 2
print(result)cube不仅是循环在此也是一个列表
查看全部 -
list 删除函数 pop()
L = ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Candy', 'David', 'Ellena']
name = L.pop()
print(name) # ==> Ellena
print(L) # ==> L = ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Candy', 'David'查看全部 -
list 列表添加新元素 append()将新元素添加到最后一位
names = ['Alice', 'Bob', 'David', 'Ellena']
names.append('Candy')
print(names) # ==> ['Alice', 'Bob', 'David', 'Ellena', 'Candy'insert ()
names = ['Alice', 'Bob', 'David', 'Ellena']
names.insert(2, 'Candy')
print(names) # ==> ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Candy', 'David', 'Ellena']查看全部 -
变量名由大小写英文字母、数字和下划线_组成
变量不能用数字开头
变量尽量不要和Python关键字重合(比如前面学习过的:and、or、not,否则可能导致Python原有关键字发挥不出作用)查看全部 -
整数:二进制(0b)、十进制、十六进制(0x)
浮点数:小数
字符串:单引号或者双引号括住任意文本
布尔值:true、false(运算方法 与或非)
空值:none查看全部 -
3.8 Python的字符串编码
python3中,默认使用UTF-8 Unicode来进行编码
查看全部 -
面向对象的编程语言
查看全部 -
非运算
在Python中,布尔类型还可以与其他数据类型(字符串,数字等)做 and、or和not运算,请看下面的代码:
a = True
print(a and 0 or 99) # ==> 99得到的计算结果不是布尔类型,而是数字99
因为Python把0、空字符串和None看成False,其他数值和非空字符串都看成True,所以:
True and 0计算结果是0
继续计算0 or 99计算结果是 99
因此,结果是99。
需要注意的是,not计算的优先级是高于and和or的。True and not False # ==> True
在上述布尔计算中,先计算not False = True,然后再计算True and True,因此得到True的结果。
短路计算
Python解释器在做布尔运算时,只要能提前确定计算结果,它就不会往后算了,直接返回结果。
查看全部 -
四则运算
整数、浮点数可以直接进行四则运算。
整数和浮点数运算后 ,得到的结果不管小数点后是否有值,结果都变成浮点数了
# 加法
num1 = 10
num2 = 0.5
result = num1 + num2
print(result) # ==> 10.5
# 减法
result = num1 - num2
print(result) # ==> 9.5
# 乘法
result = num1 * num2
print(result) # ==> 5.0
# 除法
result = num1 / num2
print(result) # ==>20.0取模运算(取余数)
Python数字支持取模运算,使用百分号%表示取模。
恰当使用取模运算,可以判断一个数是否为偶数,当一个数对2取模结果为0时,则这个数为偶数,否则为奇数。
print(3 % 2) # ==> 1 因此3为奇数
print(33 % 2) # ==> 1 因此33为奇数
print(100 % 2) # ==> 0 因此100为偶数地板除
除了普通除法以外,还有一个特殊的除法被称为地板除,对于地板除,得到的结果会忽略纯小数的部分,得到整数的部分,地板除使用//进行。
10//4 # ==> 2
10//2.5 # ==> 4.0
10//3 # ==> 3小数点位数
可以使用round()函数来处理,两个参数,第一个是需要保留小数点位数的数值,第二个是保留的位数。
num = 10 / 3
print(num) # ==> 3.3333333333333335
# 使用round保留两位小数
round(num, 2) # ==> 3.33查看全部 -
合法的变量名
变量名由大小写英文字母、数字和下划线_组成
变量不能用数字开头
变量尽量不要和Python关键字重合
定义变量
一个变量可以先后存储多种不同类型的数据。
a = 1 # 这个时候a存储的是整数类型
print(a)
a = 'ABC' # 这个时候a存储的是字符串类型
print(a)这是Python这类语言特有的特性,我们称之为动态语言,与之对应的是静态语言,Python、Javascript等等都是动态语言,Java、C、C++等等属于静态语言。
查看全部 -
整数
Python可以处理任意大小的整数
二进制整数使用前缀0b表示,比如:0b0110,0b1100
十六进制使用前缀0x,比如:0x12ef,0xde2431af
浮点数
在Python中,把10用e替代,比如:1.23x10^9就是1.23e9,或者12.3e8,0.000012可以写成1.2e-5
整数和浮点数在计算机内部存储的方式是不同的,整数运算永远是精确的,而浮点数运算则可能会有四舍五入的误差
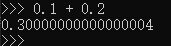
字符串
字符串是以''或""括起来的任意文本,比如'abc',"xyz"
布尔值
True、False
布尔值可以用and、or和not运算(注意and,or,not都是Python语言本身的关键字)。
and运算是与运算,只有所有都为 True,and运算结果才是 True。
or运算是或运算,只要其中有一个为 True,or 运算结果就是 True。
not运算是非运算,它是一个单目运算符,把 True 变成 False,False 变成 True。
空值
空值是Python里一个特殊的值,用None表示。
注意,None和0是不一样的,None不能理解为0,因为0是有意义的,比如我有0个苹果表示我没有苹果,0表达的是数值0的意思,而不能表示为我有None个苹果,None是一个特殊的空值。
查看全部 -
# Enter a code
num = 0
L = ['Alice', 66, 'Bob', True, 'False', 100]
for item in L:
num = num + 1
if num % 2 == 0:
print(item)
查看全部 -
dict查找速度快
python遍历dict,打印出一个完整的dict,我们需要把dict中m打印出来,比如成绩超过(这种使用for循环),并通过满足条件打印出来
for key in d 2.dict 提供items()会返回所有的dict中的元素
value=d[key] 每个元素包含key和value;for key ,value in d. items if value> 60 ()
print(key,value)
查看全部 -
元组支持切片
定义元组的方式使用()
tuple和list是不一样的,tuple是每一个元素固定不变的 ,同时不能往tuple中添加数据 而list可以的
查看全部
举报







